Regaining independence after stroke with Neurophysiotherapy:
Neurophysiotherapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation process after a stroke, helping individuals regain lost function and improve their quality of life. Here are some ways in which neurophysiotherapy can help after a stroke:
1. Motor Function Recovery: Neurophysiotherapy focuses on improving motor function and movement abilities affected by the stroke. Therapists work on strengthening weak muscles, retraining coordination and balance, and facilitating proper movement patterns. Through specific exercises and techniques, they aim to restore mobility and regain independence.
2. Muscle Tone Management: After a stroke, some individuals may experience muscle stiffness or spasticity, while others may have reduced muscle tone. Neurophysiotherapists employ various techniques, such as stretching, range of motion exercises, and muscle relaxation techniques, to manage and improve muscle tone. This helps prevent contractures, maintain joint flexibility, and enhance overall movement.
3. Balance and Postural Control: Stroke can significantly affect balance and postural control, leading to an increased risk of falls. Neurophysiotherapists design targeted exercises and training programs to improve balance and stability. This may include activities that challenge balance, weight-shifting exercises, and strengthening core muscles to enhance postural control and reduce the risk of falls.
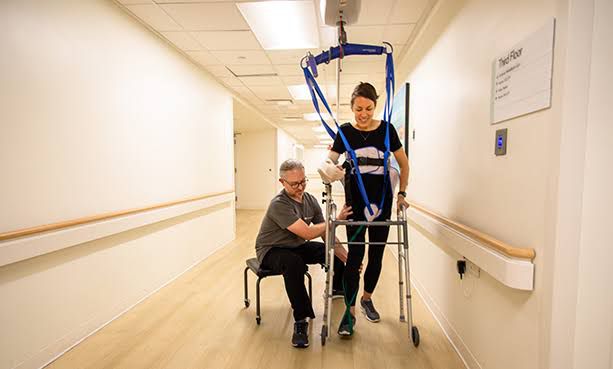
4. Gait Training: Walking difficulties are common after a stroke, but neurophysiotherapy can address gait impairments effectively. Therapists focus on improving walking patterns, step length, and symmetry. They may use assistive devices, if needed, and employ techniques such as weight shifting, rhythmic cueing, and task-specific training to enhance gait and promote a more natural walking pattern.
5. Functional Independence: Neurophysiotherapy aims to help individuals regain the functional abilities required for daily activities. Therapists work on improving hand and arm function, facilitating activities like dressing, grooming, and feeding. They also address cognitive impairments by incorporating functional tasks that promote problem-solving, memory, and attention.
6. Psychological Support and Motivation: Stroke recovery can be emotionally challenging. Neurophysiotherapists provide essential emotional support and motivation throughout the rehabilitation process. They help individuals set achievable goals, celebrate progress, and maintain a positive mindset, promoting overall well-being.
7. Education and Self-Management: Neurophysiotherapists educate patients and their caregivers about stroke, its effects, and self-management techniques. They provide guidance on exercises and strategies that can be continued at home, empowering individuals to actively participate in their recovery journey.
It is important to note that the specific approach and techniques used in neurophysiotherapy may vary based on individual needs and the stage of stroke recovery. A comprehensive assessment by a neurophysiotherapist helps determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individuals condition and goals.